Mozart's life: From child prodigy to the pinnacle of his musical genius.
Contents
Between imperial mandate and archiepiscopal tristesse
After his return from Italy, Mozart is commissioned by Empress Maria Theresa to compose a serenata for the wedding of her son Archduke Ferdinand. Mozart and his father travel to Milan, where the “Ascanio in Alba” is premiered. The 15-year-old Mozart composes the work in just three and a half weeks.
Despite his previous success in Italy, 1772 was a rather disappointing year for Mozart. Although he was offered a position as concertmaster to the new Archbishop of Salzburg, Hieronymus Franz Joseph Count von Colloredo, the pay was low. Mozart and his father continued to travel in search of further engagements. In Italy, Mozart composed the opera “Lucio Silla” and “Exsultate, jubilate”. Travels to Vienna and Munich did not lead to a permanent position, but Mozart was able to expand his knowledge and compose new works. By the age of 20, he had already created 300 compositions, including ten operas. The strained relationship with the archbishop finally led to a break in 1777.
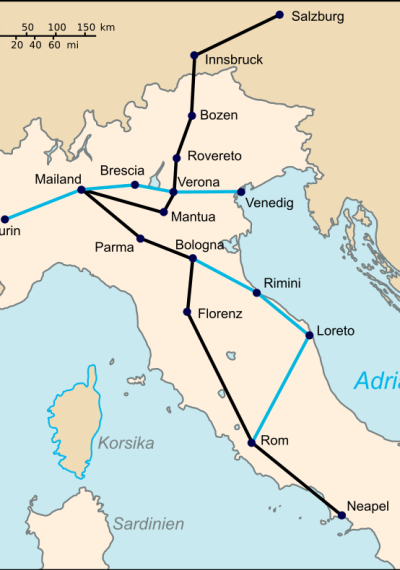
In search of fame and love
Mozart travels through Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg with his mother in search of a job. In Mannheim, he falls in love with Aloysia Weber and accompanies her family on a concert tour instead of traveling to Paris as planned. His father, dissatisfied with this development, sends his wife to bring Mozart back. Despite the success of his concerts, Mozart is not offered a permanent position. Eventually, mother and son travel to Paris, which is regarded as a center for art and culture.

Mozart's time of suffering in Paris: rejection, poverty and the loss of his mother
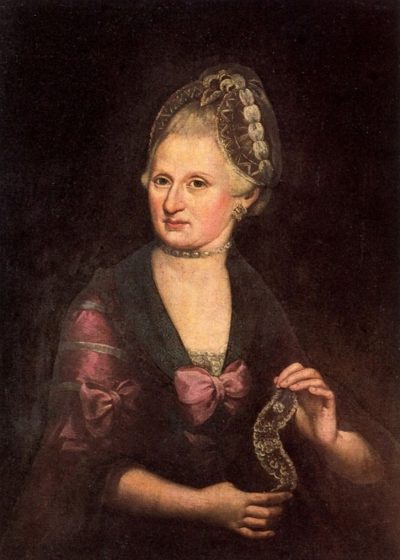
Mozart’s stay in Paris was characterized by difficulties. Despite his talent, he was repeatedly rejected by the French aristocracy. Financial problems forced him and his mother to live in poverty. After months of privation, Anna Maria Mozart became very ill. For two weeks, her condition worsened, she fantasized and eventually lost her hearing. On July 3, 1778, she died in a Parisian inn while her son watched at her bedside. The death of his beloved mother was a heavy blow for Mozart, which shook him to the core and marked a turning point in his life. These experiences, especially the loss of his mother, are reflected in his mature music.

Mozart's path to freedom: from Salzburg to Vienna
After a difficult time in Paris, Mozart returned to Salzburg, where he again had conflicts with the archbishop. This eventually led to his dismissal and a move to Vienna in 1780, where he established himself as a freelance composer and teacher, married Constanze Weber and celebrated successes such as the opera “Die Entführung aus dem Serail”. His Viennese house became a lively center for music and socializing, and he developed a friendship with Joseph Haydn.

Triumph and tragedy in waltz time
In the years following his move to Vienna, Mozart created some of his most famous works, including “The Marriage of Figaro” (1786). Although the premiere in Vienna was not successful, the opera was celebrated in Prague and led to a commission for “Don Giovanni”.
In 1787, Mozart’s father Leopold died, which shook him to the core. Despite grief and financial difficulties, he completed “Don Giovanni”. At the same time, the young Beethoven came to Vienna to study with Mozart, but the plan fell through due to unfortunate circumstances.
Despite personal losses, Emperor Joseph II appointed Mozart imperial-royal chamber musician, which offered him financial security. Mozart continued to compose successfully and premiered “Così fan tutte” in 1790 and “La clemenza di Tito” and “The Magic Flute” in 1791.
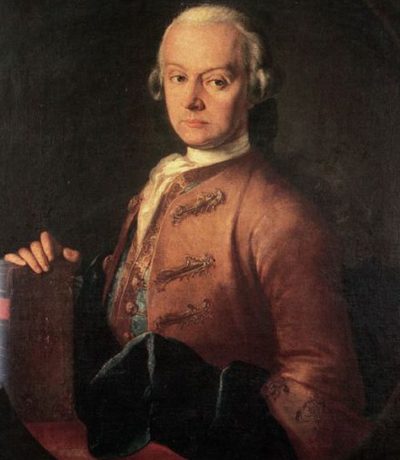
Mozart and Constanze: love and destiny
Mozart was not a handsome man, but his self-confidence and sense of humor gave him a certain charm. He had many affairs before marrying Constanze, after his first love Aloysia had rejected him. Mozart and Constanze had a happy marriage, characterized by their shared passion for music and Constanze’s support for Mozart’s work. They had six children, only two of whom reached adulthood. Despite Mozart’s lavish lifestyle and Constanze’s health problems, they lived a comfortable life.
Last act of a genius
In 1791, Mozart, who was already ailing, received a commission for a requiem. Plagued by gloomy premonitions, he worked feverishly on the work, which reflected his own fate. Between the triumphs of his last operas, he struggled with illness and exhaustion.
In November, his condition deteriorated dramatically. Despite the successful premiere of the “Magic Flute”, he succumbed to his illness on December 5, 1791. His unfinished Requiem remains as the legacy of a tormented genius whose death shrouded the music world in grief.

Frequently asked questions about Mozart answered
What was Mozart like?
Mozart was a genius, but also an eccentric and expressive person who was often plagued by depression. Although he was artistically very mature, he remained childlike in everyday life and was unable to manage money or structure his life. However, his music remains unsurpassed to this day and is known worldwide. Many of his pieces are iconic and give listeners goosebumps. Mozart is and remains an unforgettable composer.
How many compositions are there by Mozart?
At the age of 20, Mozart had already created over 300 compositions, and by the end of his life there were more than 600. The Köchelverzeichnis, which was compiled in 1862, lists 626 of his works.
What are Mozart's most famous compositions?
Mozart left behind a rich musical legacy, including numerous melodies that are familiar to us without us consciously associating them with him. Here are seven of his best-known works, arranged chronologically:
- Idomeneo KV366 (1781): Mozart’s personal favorite
- The Marriage of Figaro KV492 (1786)
- The Little Night Music KV525 (1787)
- Don Giovanni KV527 (1787)
- Così fan tutte KV588 (1790)
- The Magic Flute KV620 (1791)
- Requiem KV626 (1791)
Which instrument did Mozart play?
Mozart was a musical prodigy who mastered both the piano and the violin. He showed his extraordinary talent on the piano at the age of four, while his father actually taught his sister Nannerl. Shortly afterwards, he began piano lessons and soon gave his first concerts together with his sister. At the age of seven, he was given a violin and spontaneously played the second part almost perfectly without ever having had any lessons.
Did Mozart know Beethoven?
Beethoven, fourteen years younger than Mozart, traveled to Vienna in 1787 as a sixteen-year-old musically gifted teenager to take lessons from Mozart or Haydn. Unfortunately, Mozart was unable to receive him due to a lack of time, and Beethoven had to return to Bonn after just two weeks due to his mother’s illness. This led to a close encounter between the two composers, which almost prevented them from working together.
Who was Mozart a friend of?
- Marie Antoinette: As a child, Mozart played at the court of Versailles with Marie Antoinette, who was the same age. However, this carefree friendship ended when Mozart was no longer a child prodigy and the future queen no longer showed any interest in him.
- Johann Christian Bach: In his youth, Mozart developed a close friendship with Johann Christian Bach, the son of Johann Sebastian Bach. Bach became an important mentor for the young Mozart.
- Joseph Haydn: Mozart had a particularly deep friendship with Joseph Haydn, who was 24 years older than him. Haydn became a father figure for Mozart, a Leader and friend. Mozart dedicated six string quartets to Haydn, and both were members of the masonic lodge “Zur wahren Eintracht”.
These friendships had a decisive influence on Mozart’s life and artistic development and give us an insight into the social environment of one of the greatest composers of all time.
Has our article aroused your interest in Mozart?
Viennese classical music at its best
